
Scientists from three Polish scientific and research institutions described substitutes for expensive precious metals for use in the production of clean power. The materials for catalysis are inspired by natural metalloproteins.
“Expensive catalysts based on platinum are currently used in many chemical processes. And yet nature can catalyse similar chemical processes with common base metals such as iron or manganese,” explain Dr. Wojciech Kiciński, Dr. Sławomir Dyjak and Mateusz Gratzke from the Military University of Technology, Dr. Wojciech Tokarz from the Łukasiewicz - Industrial Chemistry Institute and Dr. Artur Błachowski from the AGH University of Science and Technology, co-authors of the paper published in the journal Fuel.
They investigated the possibility of synthesising materials that could replace expensive precious metals used in the catalysis of fuel synthesis processes and their use for electricity production.
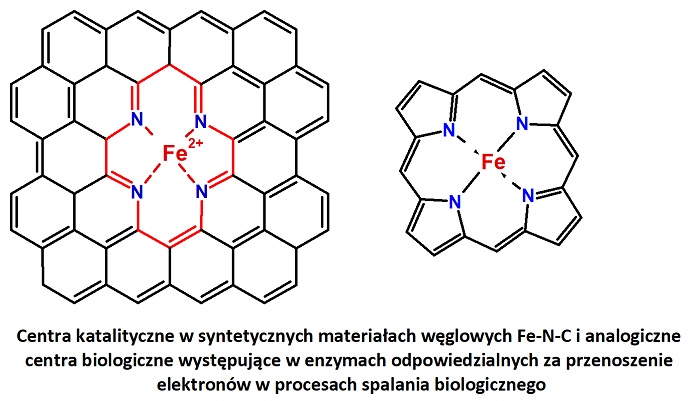
In an interview with PAP, the first author of the paper Dr. Wojciech Kiciński gives an example of a carbon material doped with nitrogen and iron. The material has properties similar to naturally occurring enzymes and proteins performing important life functions in the process of biological fuel combustion.
“Such materials are a competition for platinum and palladium used in devices for generating electricity from chemical energy contained, for example, in hydrogen fuel. Ultimately, they can be used in components of hydrogen-powered electric cars,” the scientist predicts.
The research work was done as part of the OPUS-19 grant 'Porous carbon materials with mononuclear coordination centers of the Fe-N4 type: universal (electro) catalysts for electroprotic reactions' financed by the Polish National Science Centre.
PAP - Science in Poland, Karolina Duszczyk
kol/ zan/ kap/
tr. RL













