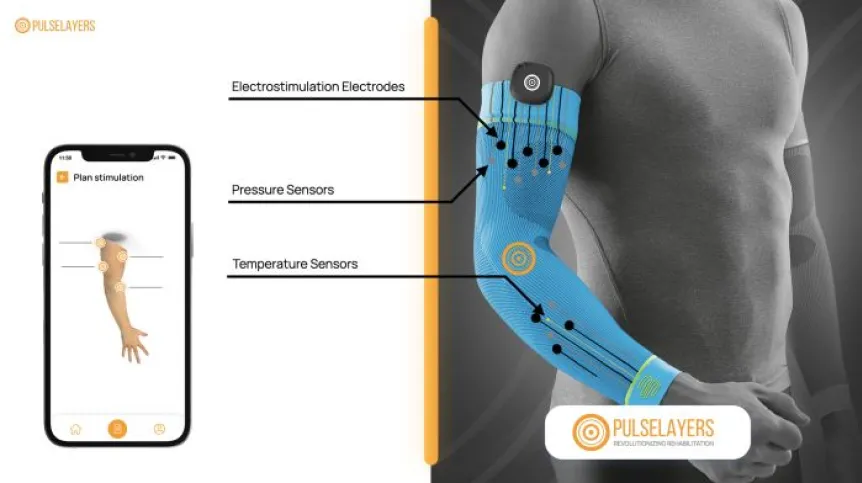
An electrostimulating dressing with temperature and pressure sensors can shorten the time of recovery after a limb fracture and make it less burdensome. PulseLAYERS is an idea of doctoral candidates from the Warsaw University of Technology.
PulseLAYERS is a specialised dressing worn over the fracture site. It contains sensors and electrodes responsible for electrostimulation. The authors of the idea use printed electronics - an increasingly popular method of manufacturing electronic components on various substrates. This method requires the development of detailed pastes, but is efficient and has a very wide range of applications, the doctoral candidates from the Warsaw University of Technology assure.
'Our solution reduces the atrophy of the patient's muscles during the fractured limb's re-growth and makes it possible to limit the onerous and difficult rehabilitation process to a minimum. It also reduces the risk of complications related to bone fusion and speeds up healing,’ says team leader Dominik Baraniecki, quoted in the university press release.
Any immobilisation of a limb is associated with an inevitable loss of muscle mass. After six weeks, it can amount to approximately 20 percent. Research confirms that electrostimulation can effectively counteract this loss. In addition. it has a positive effect on the healing process itself.
'We plan to raise funds in the form of grants or ongoing research and development projects in order to bring the device to the level of proof of concept and possible implementation,’ says Baraniecki.
The authors of the PulseLAYERS are: Dominik Baraniecki, Filip Budny, Jan Dominiczak, Aleksandra Kądziela, Łukasz Nowicki and Izabela Wojciechowska. The young scientists presented their idea during Tech-Athon, a polytechnic marathon of work on innovative solutions with implementation potential. The team won an award and PLN 30 000 for the development of the idea in this competition. (PAP)
PAP - Science in Poland
kol/ bar/ kap/
tr. RL













