-

Expert: People have no reason to fear wolves
Many reports of wolf attacks on animals are simply fake news, says mammal expert Katarzyna Kozyra-Zyskowska, PhD. She emphasises that people currently have no reason to fear wolves.
-

City full of ticks: New study in Warsaw
Ticks are not only a problem of forests and meadows. New study by scientists from the University of Warsaw confirms that these parasites are also very common in cities: in parks, botanical gardens, on private properties, and even kindergarten grounds. On top of that, they become active earlier than is commonly believed.
-

Expert: Argo floats can be confused with torpedoes
Meter-long, cylindrical, with a protruding antenna, underwater oceanographic Argo robots collect data about the Baltic Sea. They have been accidentally caught, causing concern because their shape resembles a torpedo. That is why the Institute of Oceanology of the Polish Academy of Sciences places clear markings on them, says oceanographer Daniel Rak, PhD.
-

Study: Wolves prefer wild ungulates to cattle and horses
Despite the presence of several thousand free-grazing cows and several hundred horses in the Warta River Mouth area, wolves prey there primarily on wild mammal species, scientists from the Faculty of Biology of the University of Warsaw have shown. According to the researchers, this due to the way the livestock is grazed and the fact that cows are not dehorned.
-

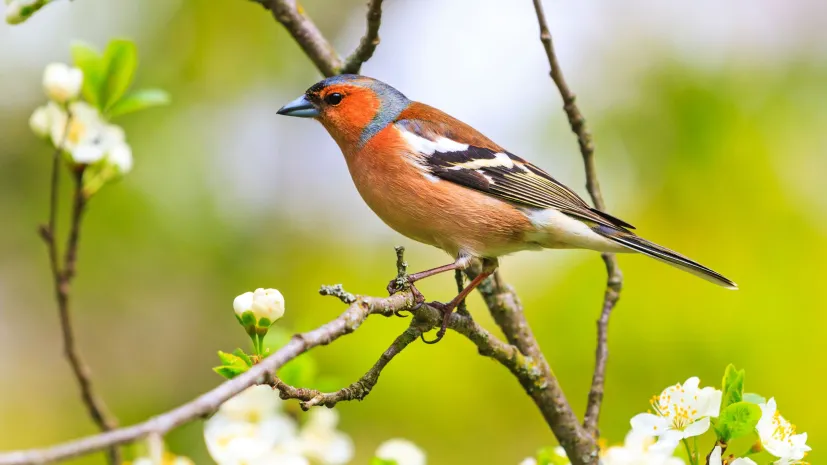
Expert: Birds compete for singing space like for food
Some birds adapt their sounds to the environment, others only sing in noise, Michał Budka, PhD, an eco-acoustician from the Adam Mickiewicz University says in an interview with PAP. He adds that birds compete for singing space just like they do for food or territory.
-

Alien species in the environment: piranha in the San and running bamboo over the Lubatówka
On the Lubatówka River in Poland (Podkarpacie, near Krosno), hydrobiologists have observed with concern wild thickets of Bisset bamboo, considered an alien invasive species in many parts of the world. Ecologists are also concerned about the appearance of giant miscanthus in the natural environment. A piranha has been caught in the San.
-

Hundreds of amphibian species will be pushed beyond their tolerable temperature range
At the current rate of global temperature increase, by the end of the century nearly 400 amphibian species (7.5%) will be pushed beyond their tolerable temperature range, according to an international forecast covering more than 60 percent of amphibian species.
-

Light pollution poses huge problems for plants
Light pollution affects not only humans, but also - very strongly - plants. It disrupts their growth, flowering and immunity, which affects ecosystems, crops and food production. Meanwhile, this is a problem that can be partially relatively easily reduced, scientists believe.
-

Scientists from University of Gdańsk discover new species of parasite
Scientists from the University of Gdańsk have discovered a new species of mite. It is a skin parasite that caused serious symptoms in the head of the Senegal galago.