
In the soils where wild raspberries naturally resistant to some diseases grow, researchers have found strains of fungi that help plants become immune to dangerous pathogens. Now they have developed a blend of fungi and supplements to help growers protect their raspberries and strawberries.
Researchers from Professor Magdalena Frąc's team (Institute of Agrophysics of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Lublin) decided to focus on four types of pathogens - important problems for raspberry growers. Botrytis fungi cause grey mold in raspberries and strawberries, Colletotrichum - fruit anthracnose (manifested by the formation of black spots, among other things), and Verticillium and fungus-like organisms of the genus Phytophthora attack the root of seedlings and then destroy the plant.
Scientists looked for natural allies of raspberries - soil microorganisms that would inhabit the ecological niche that pathogens tended to enter. The assumption was: if the soil were inhabited by 'friendly' fungi, there would be no place for the development of other pathogenic fungi. And the plant would be supported in defence against pathogens.
Professor Frąc said: “We cooperated with forest districts that helped us select places with natural raspberry habitats. We searched for wild raspberries that developed healthily, despite the fact that they were not fertilized or sprayed. That means a natural disease resistance. We travelled to many places in the Lublin, Mazovian, Kuyavian-Pomeranian and other provinces of Poland. We took samples, characterized the habitats, collected and marked the microbiome from the rhizosphere (the root zone).”
The scientists tested about 200 strains of fungi. They searched for those that would be the most effective in combating pathogens and be safe for humans, plants and the environment.
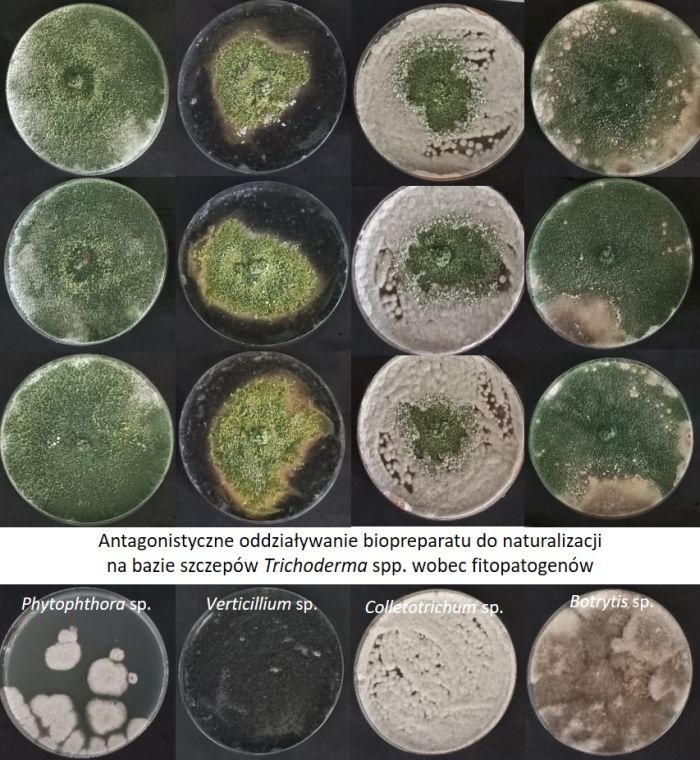
The preparation developed by Polish researchers includes 11 strains of Trichoderma fungi (a genus that is a source of strains effective in supporting growth and biological protection of plants). These strains have been selected so that they would not compete with each other and coexist peacefully instead.
In addition to fungal spores, the preparation also contains a properly prepared supplementary mixture that will facilitate the rapid development of selected fungi, but will not be conducive to the development of phytopathogenic fungi.
Professor Frąc said: “We developed two formulations. One is poured under the roots of seedlings at newly established plantations. The other can be dissolved in water and used as a spray on the leaves or at the root for naturalization watering.
“We assessed under controlled conditions how the preparation would affect plant development. We showed that in the case of the grey mould pathogen, control plants - not naturalized - died. Plants watered with the product or treated with a combined naturalization strategy of plant and root inoculation dealt with the pathogen and developed normally.”
She added: “The patent application describes the method of producing the biopreparation. We know exactly how to grow these selected wild strains of fungi, process them and stimulate their development.”
The study is part of the EcoFruits project financed in the BIOSTRATEG programme of the National Centre for Research and Development.

In December 2022, Professor Magdalena Frąc's team from the Institute of Agrophysics of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Lublin and the Institute of Horticulture-NRI received the distinction of the II Department of the Polish Academy of Sciences for research on improving the functional and structural biodiversity of soil microorganisms for sustainable and ecological agriculture (including publication in the International Journal of Molecular Science). (PAP)
PAP - Science in Poland, Ludwika Tomala
lt/ agt/ kap/
tr. RL













