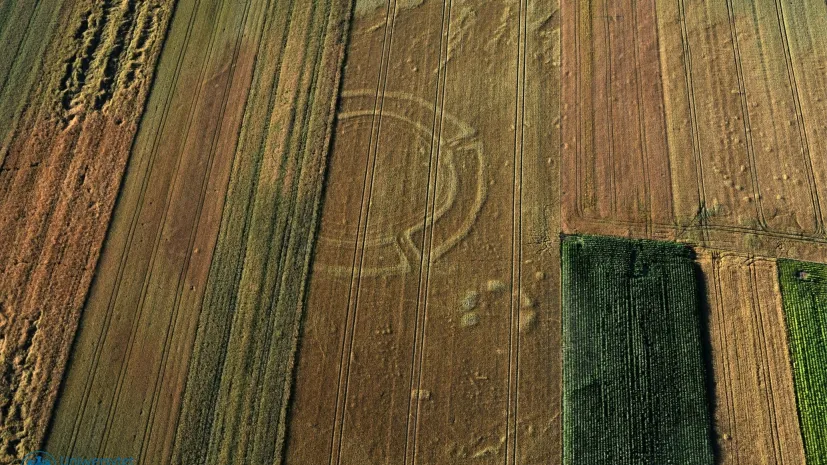
Twenty-five years after discovery of 'Polish Stonehenge' we now know about 20 other such structures
Monumental structures dating back 7,000 years and reaching over 100m in diameter, consisting of circular ditches and palisades, remained unknown in Poland until the 1990s. It has been 25 years since the discovery of the first structure of this type, sometimes referred to as the 'Polish Stonehenge'. To date, approx. 20 of them have been identified.
-

Georgia/Polish scientists: Legio X Fretensis was stationed at Apsaros in Colchis
In the early 2nd century CE, soldiers from Legio X Fretensis, known for their bloody suppression of Jewish uprisings, were also stationed on the Black Sea, in the Roman fort Apsaros in Colchis, Polish researchers have found. Until now scientists did not know traces of their presence in such a remote area.
-

Archaeologists discover traces of prehistoric settlements Mikołajki
Traces of prehistoric and late medieval settlements were discovered during excavations in Mikołajki, the monument conservation services announced Monday. Archaeologists discovered a granite stele that could be a place associated with ancient beliefs.
-

Armenia/ Large amounts of flour residue discovered in 3,000 years old building
Large amounts of flour residue from 3,000 years ago have been discovered by a Polish-Armenian team of archaeologists working in Metsamor, Armenia. The discovery was made in a large building supported on columns, which collapsed during a fire.
-
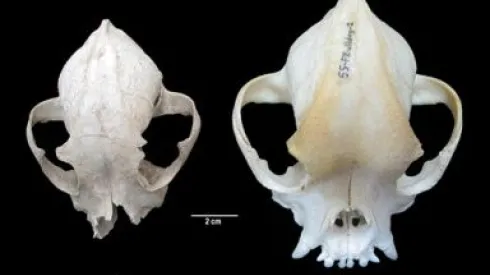
Scientists prove that Romans were breeding small bulldogs
Researchers from the Wrocław University of Environmental and Life Sciences have proven that breeding small brachycephalic (shorter-nosed) dogs took place already in ancient Rome. Research on a 2,000 years old dog skull indicates that the dog resembled a French bulldog.
-

Lublin Province/ Detectorists find 3.5 thousand years old dagger in forest
Detectorists searching the forest near Krasnystaw (Lubelskie) found an approx. 3.5 thousand years old bronze dagger. According to the conservator Paweł Wira, the scientific value of the find is enormous.
-

Archaeologists discover ‘unique’ paintings in Old Dongola
A team of archaeologists led by Dr. Artur Obłuski from the Polish Centre of Mediterranean Archaeology, University of Warsaw, has discovered a complex of rooms, the interiors of which were covered with figural scenes unique for Christian art.
-

Article about University of Warsaw archaeology research was most read article in Science News in 2022
An article about the research of Dagmara Socha from the Centre for Andean Studies of the University of Warsaw was the most read text in Science News in 2022, the University of Warsaw reports.
-

Neolithic farmers processed cow, goat and sheep milk, says new study
Farmers living in today’s Poland during the Neolithic period produced dairy products from the milk of various animals: cows, sheep and goats. This was confirmed by analyses of residues from clay vessels found in the Kujawy-Pomerania Province. The research results have been published in the Royal Society Open Science.
-

Discovery of blocks with hieroglyphic inscriptions in Old Dongola could move city's history back 1,000 years
Polish archaeologists discovered sandstone blocks from a Pharaonic temple covered with hieroglyphs during excavations in Old Dongola in Sudan. The blocks come from the first half of the first millennium BCE. So far, no ruins from such an early period have been found there; this could move the city's history back a thousand years.