-

Ancient DNA study shows massive migration shaped Slavic origins and changed the shape of Europe
Between the 6th and 8th centuries CE, more than 80% of people in eastern Germany, Poland, Ukraine, and the northern Balkans were newcomers from the East, according to an international study of ancient DNA published in Nature.
-

Young researchers use AI but remain wary, study finds
Young researchers are embracing artificial intelligence tools but remain cautious about their reliability, according to findings from the international research initiative Harbingers of Change.
-

Polish team to lead international study of pre-industrial pandemics
Scientists at the Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń will investigate pandemics that swept Europe between 1350 and 1800, combining historical data with DNA analysis from human remains.
-

Polish, Japanese and Indian scientists develop colour-changing stress-sensitive material
Researchers from the AGH University of Science and Technology in Kraków, working with partners from Japan and India, have developed a smart material that changes colour when subjected to mechanical stress. The invention could be used to prevent structural failures, the scientists said.
-

Health and personal goals main motivations of long-distance runners, study finds
Health and personal achievement are the strongest motivations for people taking part in long-distance road races, according to research published in Social Sciences by scientists from the Medical University of Silesia.
-
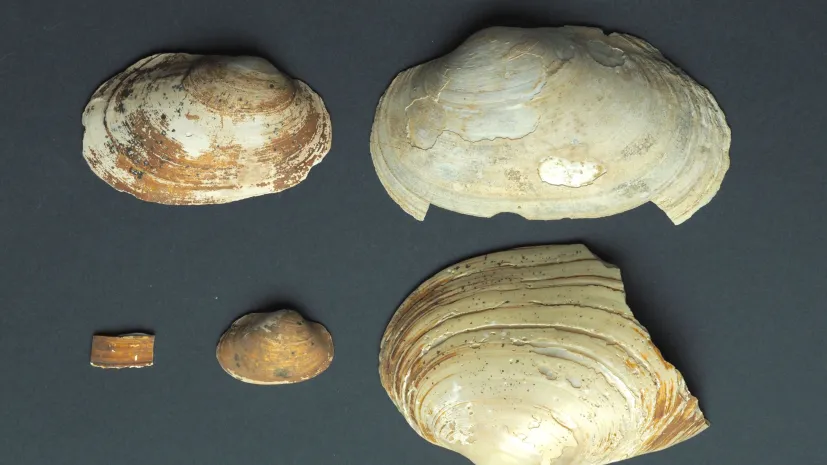

Polish researchers investigate ancient necropolis shells to reveal lives of Ancient Egyptians
Mollusc shells uncovered at Egypt’s Saqqara necropolis are providing archaeologists with new insights into the customs, beliefs, and daily life of ancient Egyptians. The finds come from the Saqqara West mission, a Polish-led excavation active since 1987.
-
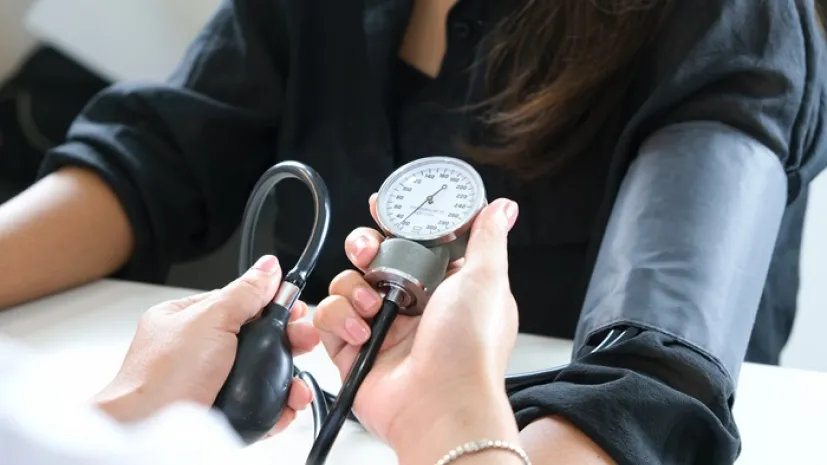

Polish researchers find link between hypertension, sleep disorders, and vitamin D
Patients with hypertension have poorer sleep quality than those with normal blood pressure, according to a study by researchers from Wrocław Medical University and the Wrocław University of Environmental and Life Sciences.
-

Baby boomers more eco-friendly than younger generations, Polish study finds
Contrary to popular belief, younger generations are not the most environmentally conscious. New research shows that people over 60 practice the most eco-friendly habits, outpacing millennials and Generation Z.
-
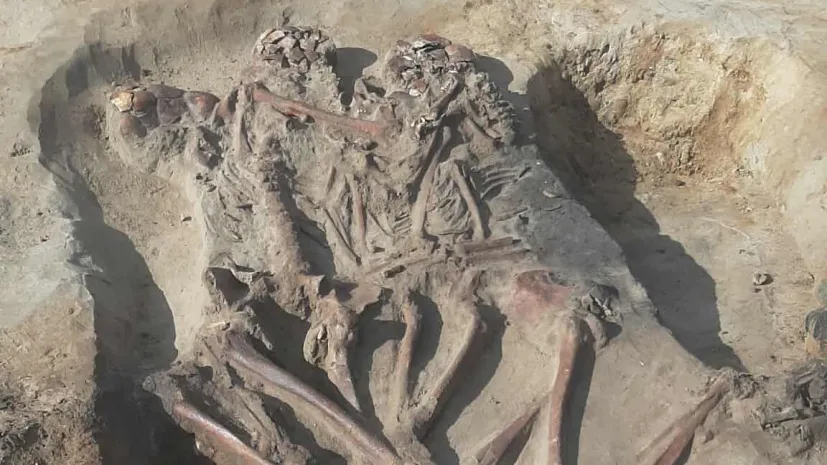

Rare Mesolithic mass burial site found during gas pipeline construction
Archaeologists have uncovered a rare Mesolithic mass burial during gas pipeline construction in Poland. The grave near the village of Orłowo in the north central Inowrocław municipality contained the remains of four people—a man, a woman, and two children—arranged as if embracing each other. The find is estimated to date back to 8000–7000 BCE.