
Scientists from the Kraków University of Technology, in collaboration with researchers from research centres in Kraków and Lublin, have discovered a new method of removing drugs from the body. According to them, the method is safe and effective.
The researchers led by Dr. Przemysław Jodłowski from the Faculty of Chemical Engineering and Technology at the Kraków University of Technology proposes using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as carriers for drugs from the group of β-blockers, used to detoxify the body from narcotics.
The scientists described the effects of their work on an innovative method of propranolol administration in mephedrone overdose in the prestigious Chemical Engineering Journal.
The researchers point out that mephedrone has been a particularly dangerous narcotic substance in recent years. The compound, included in the group of synthetic cathinones, imitates amphetamine in its structure and effect. Although it was outlawed in 2010, it remains popular in the illicit trade due to its relatively low price and high availability on the black market. Its overdose, however, can lead to severe health and even life-threatening risks.
β-blockers are used for detoxification after poisoning with this drug. 'The problem to be solved in the context of the use of drugs from the β-blocker group in mephedrone intoxication was to find a suitable carrier that would release the drug safely and effectively - that is, gradually and directionally, while excluding the effect of the first passage of the drug. This effect results in the elimination of the drug from the body (by metabolic processes taking place, for example, in the intestinal mucosa and liver) before getting into the systemic circulation,’ Jodłowski says.
Under his supervision, an interdisciplinary team of researchers from the Kraków University of Technology, the Jagiellonian University, the AGH UST of Kraków, the Medical University of Lublin and the Institute of Rock Mass Mechanics of the Polish Academy of Sciences developed an effective and innovative detoxification system for the body, solving these problems.
The scientists conducted the research as part of the project 'Modern materials based on metal-organic networks for the removal of psychoactive substances - synthesis, chemical characterisation, toxicity and efficiency for in vitro and in vivo studies', funded by the Polish National Science Centre in the OPUS 22 competition.
Dr. Jodłowski explains that the proposed method involves using metal-organic networks to remove drugs from the body. 'Thanks to their characteristics, a sudden reaction of the body to the administration of the antidote can be avoided. The use of metal-organic networks - thanks to the possibility of their modification - allows for controlled drug adsorption and controlled administration of the antidote,’ he says.
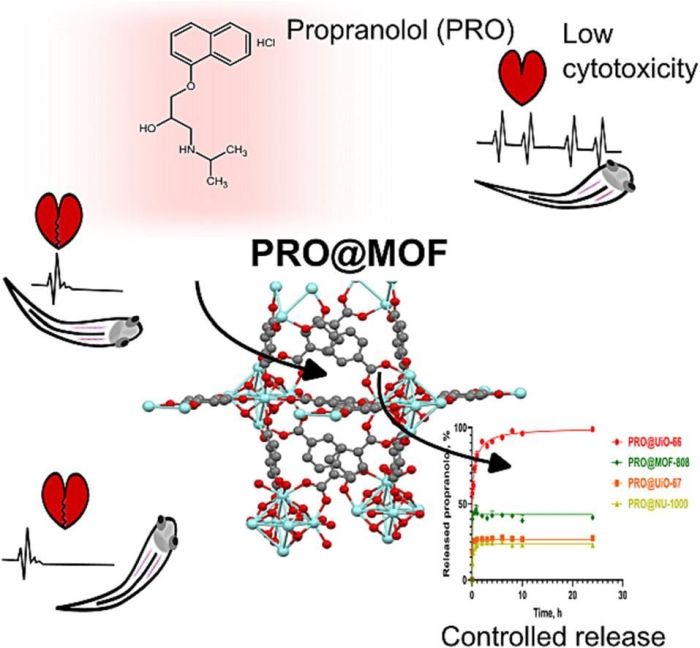
He adds that MOFs, or metal-organic networks, are substances with one-dimensional, two-dimensional or three-dimensional structures, depending on the materials used in their construction. They consist of metal ions that are joined together by organic ligands to form a crystalline structure. These materials have applications in many fields, from medicine (drug delivery, tomographic imaging) to catalysis, labelling and gas adsorption.
The research results have confirmed that the organometallic skeleton can be used as a carrier of the drug eliminating the effects of mephedrone abuse and as an adsorbent of this drug.
The research team will continue to develop its innovative method and proceed with further stages aimed at introducing it in medicine. The scientists hope that the end result of their work will be a medicine (in the form of an easy-to-use powder) that will help fight one of the pressing problems of the modern world. (PAP)
PAP - Science in Poland
rgr/ agt/ kap/
tr. RL













