-

Viral DNA triggers autoimmunity when unchecked, study finds
A large portion of the human genome is made up of viral remnants, genetic material left behind by ancient infections. New research published in Cell Reports reveals that when these sequences become overactive, they can trigger autoimmune diseases.
-

Up to 5 million Poles suffer from migraines yet treatment remains inadequate, study finds
As many as 5 million people in Poland may suffer from migraines, making the condition a significant public health and economic burden, according to the largest national study on migraine to date.
-

Polish scientists develop biodegradable bacterial sponge to clean wastewater
Researchers from the University of Silesia in Katowice have patented a novel biological preparation that improves the removal of pharmaceuticals and phenolic compounds from wastewater.
-

Ageing can be controlled, say experts
Until recently, ageing was widely regarded as an inevitable, genetically determined process. But mounting scientific evidence is challenging that notion, suggesting ageing may not only be influenced by external factors, but actively slowed.
-

Scientists advance Quantum Magnetism research with discovery of single ‘spinion’ in magnetic models
Researchers from the University of Warsaw and the University of British Columbia have identified how a fundamental quantum excitation known as a lone spinon, a single, unpaired spin, can emerge in magnetic models.
-

Warsaw Uni researchers help launch multilingual mental health platform for migrants and refugees
Migrants and refugees face serious mental health challenges, often compounded by language barriers and lack of information on how to access care.
-
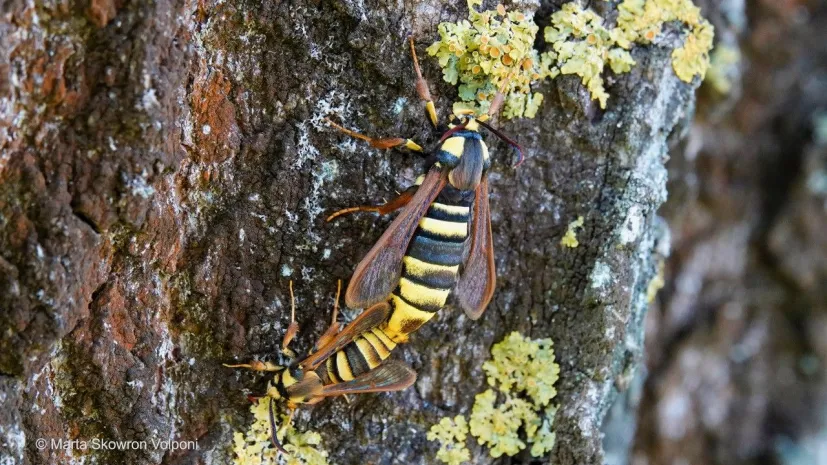

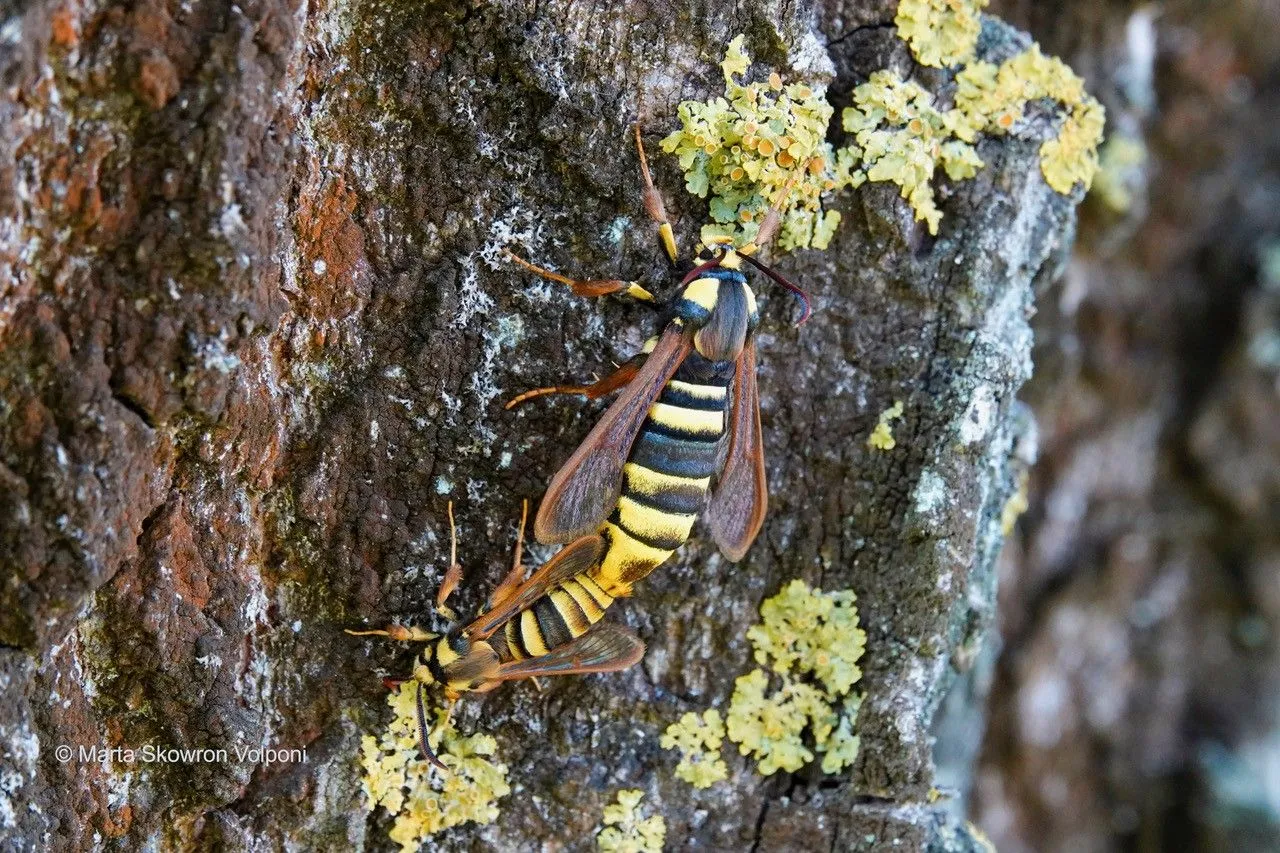
Hornet moth mimics buzz and appearance of hornets to scare off predators, study finds
The hornet moth (Sesia apiformis) has evolved not only to look like a hornet but also to sound like one, a rare form of mimicry that fools predators into keeping their distance. According to new research led by Dr. Marta Skowron Volponi from the University of Białystok, the moth’s acoustic camouflage is so effective that robins—the study’s test predators—reacted to it almost exactly as they would to a real hornet.
-
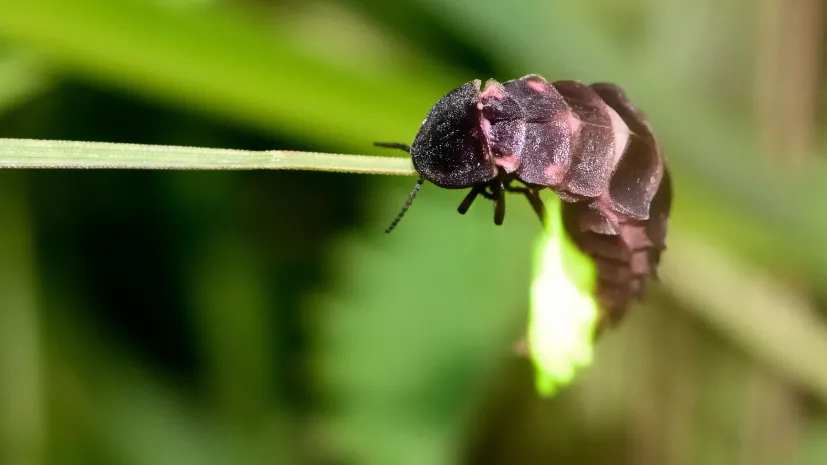

Fireflies may disappear within decades, warns naturist
Firefly populations in Poland have dropped by 30 to 70 percent over recent decades raising concerns that the insects could soon disappear entirely, says naturist Mikołaj Siemaszko.
-
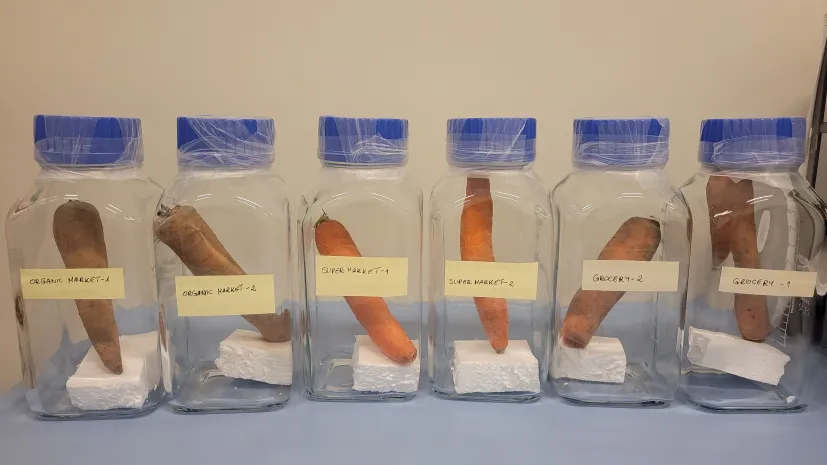
Warsaw researcher develops device to detect plant diseases early by analyzing their smell
Scientists at the Warsaw University of Technology are developing a device that can detect plant diseases early by analyzing the unique “fragrance bouquet” of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by plants.














