
Undersea observatory learns to identify cosmic signals from sea noise
KM3NeT, a vast undersea network of thousands of light sensors in the Mediterranean Sea, is learning to distinguish rare neutrino signals from natural background flashes in real time, according to a study published in Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A.
-

Geneticist warns against inbreeding of purebred dogs and sterilisation of mixed breeds
A growing focus on breeding purebred dogs while sterilising healthy mixed-breed animals is a disturbing trend that harms dogs and their owners, an evolutionary geneticist from the University of Gdańsk has warned.
-

Birds must watch every gram of fat to survive winter, says ornithologist
The next two months are the coldest and most critical for birds, making winter feeding both essential and strategically complex, according to ornithologist Konrad Leniowski, PhD, from the University of Rzeszów.
-
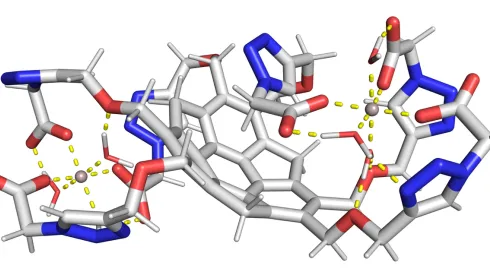
Polish chemists develop water-soluble fluorescent molecules to detect metal contaminants
Polish chemists have developed new water-soluble molecules whose fluorescence is quenched in the presence of selected metal ions, a discovery that could support faster detection of contaminants in river and lake water, researchers from the Warsaw University of Technology said.
-

Scientists turn waste into powerful water cleaner for industrial dyes
Scientists from India, in collaboration with Polish PhD Michał Piasecki from Częstochowa, have developed a porous material from agricultural and industrial waste that accelerates the decomposition of persistent dyes in wastewater under visible light.
-

Bears are adapting diets to climate change, international study finds
Bears are adapting their diets in response to global environmental changes, according to a new study by an international team of researchers, including scientists from Poland.
-

Polish biologist discovers new species of orchid in Peru’s Andes
A previously unknown orchid species has been discovered in the high Andes of Peru, growing at elevations above 3,000 metres, expanding scientific knowledge of one of the world’s most sensitive and specialized plant groups.
-

Experts Warn Europe must adopt ‘worst-case emissions scenario’ in climate plan
The Committee on the Climate Crisis of the Polish Academy of Sciences is urging that the future European Climate Adaptation Plan (ECAP) adopt the emissions worst-case scenario as a planning baseline, warning that immediate action is needed to adapt to climate change that has already occurred and to limit further warming.
-

Polygamy in dogs may have driven their domestication, study finds
The domestic dog is the only canid species whose primary mating system is polygamy, a trait that may have played a key role in its domestication and the spread of dog genes, according to a study led by a Polish researcher and published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
-

Illegal poultry carcass storage linked to rising wolf–human conflicts, study finds
Illegally stored poultry carcasses on or near farms attract wolves and increase the risk of conflicts between predators and humans, according to a new study by Polish scientists, who are calling for urgent inspections of factory farming operations.













