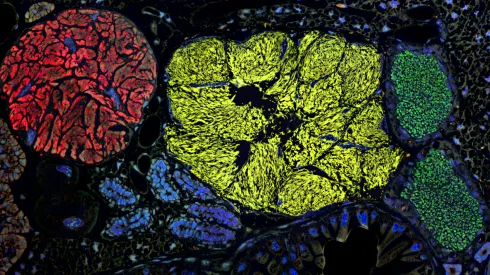
Warsaw scientists discover new function of specialized liver vascular cells
A previously unknown function of specialised liver vascular cells, showing that they actively remove free haemoglobin from the bloodstream, has been identified by scientists from the International Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology in Warsaw.
-

Polish scientists warn GFP fluorescent marker may lead to misinterpretation in cell research
Polish researchers have shown that green fluorescent protein (GFP), one of the most widely used marker proteins in biological research, may lead to misinterpretations of cellular processes.
-

Ancient three-clawed turtles roamed farther north than previously thought, study finds
Fossils of three-clawed turtles dating to about 12 million years ago have been discovered at three sites in southern Poland, significantly extending the known northern range of the group.
-

Polish scientists develop nanocomposite that produces biocides on demand
Polish scientists have developed a silica-based nanocomposite known as B-STING, that can automatically generate biocidal substances in response to microorganisms, effectively targeting bacteria, fungi, and viruses while remaining safe for human cells.
-
Polish scientists identify smallest known bacterial genomes
Polish researchers have discovered and described the smallest bacterial genomes ever identified, containing just over 60 protein-coding genes - roughly 1% of a typical bacterial genome - placing these microorganisms at the edge of cellular life.
-

Pollinator survival depends on soil quality, study finds
Pollinator survival depends on soil quality, scientists involved in a pan-European research initiative said, announcing a four-year project to examine how soil condition and management affect pollinating insects and what measures could better protect them.
-

Fungal infection alters ant colony behaviour, study shows
A long-term fungal infection in ants affects the division of labour within colonies, according to biologists from the University of Warsaw Botanical Garden and the Museum and Institute of Zoology of the Polish Academy of Sciences.
-

Giant ‘sea lizard’ the size of a killer whale found in Poland
Palaeontologists have identified the remains of a large ichthyosaur, comparable in size to a modern killer whale, discovered in a phosphate mine in Annopol on the Vistula River in eastern Poland.
-

European city birds flee sooner from women than men, study finds
Birds living in European cities flee earlier from women than from men, according to an international study that included Polish researchers.
-

Undersea observatory learns to identify cosmic signals from sea noise
KM3NeT, a vast undersea network of thousands of light sensors in the Mediterranean Sea, is learning to distinguish rare neutrino signals from natural background flashes in real time, according to a study published in Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A.













